Woooo! The doc strikes again, wonderful stuff :D
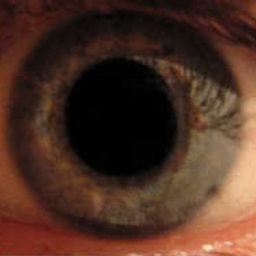
Pupillary response is a physiological response that varies the size of the pupil, via the optic and oculomotor cranial nerve. This response results in either constriction (miosis), narrowing the pupil, or dilation (mydriasis), widening the pupil. This occurs via relaxation or contraction of the iris dilator muscle respectively. The response can have a variety of causes, from an involuntary reflex reaction to exposure or inexposure to light — in low light conditions a dilated pupil lets more light into the eye — or it may indicate interest in the subject of attention, or sexual stimulation. The pupils contract immediately before someone falls asleep. A pupillary response can be intentionally conditioned as a Pavlovian response to some stimuli. The latency of pupillary response (the time in which it takes to occur) increases with age.
Use of central nervous system stimulant drugs and some hallucinogenic drugs can cause dilation of the pupil.
Source: wikipedia
original music by jonjon
4 Comments
Create an account or Login to write a comment.